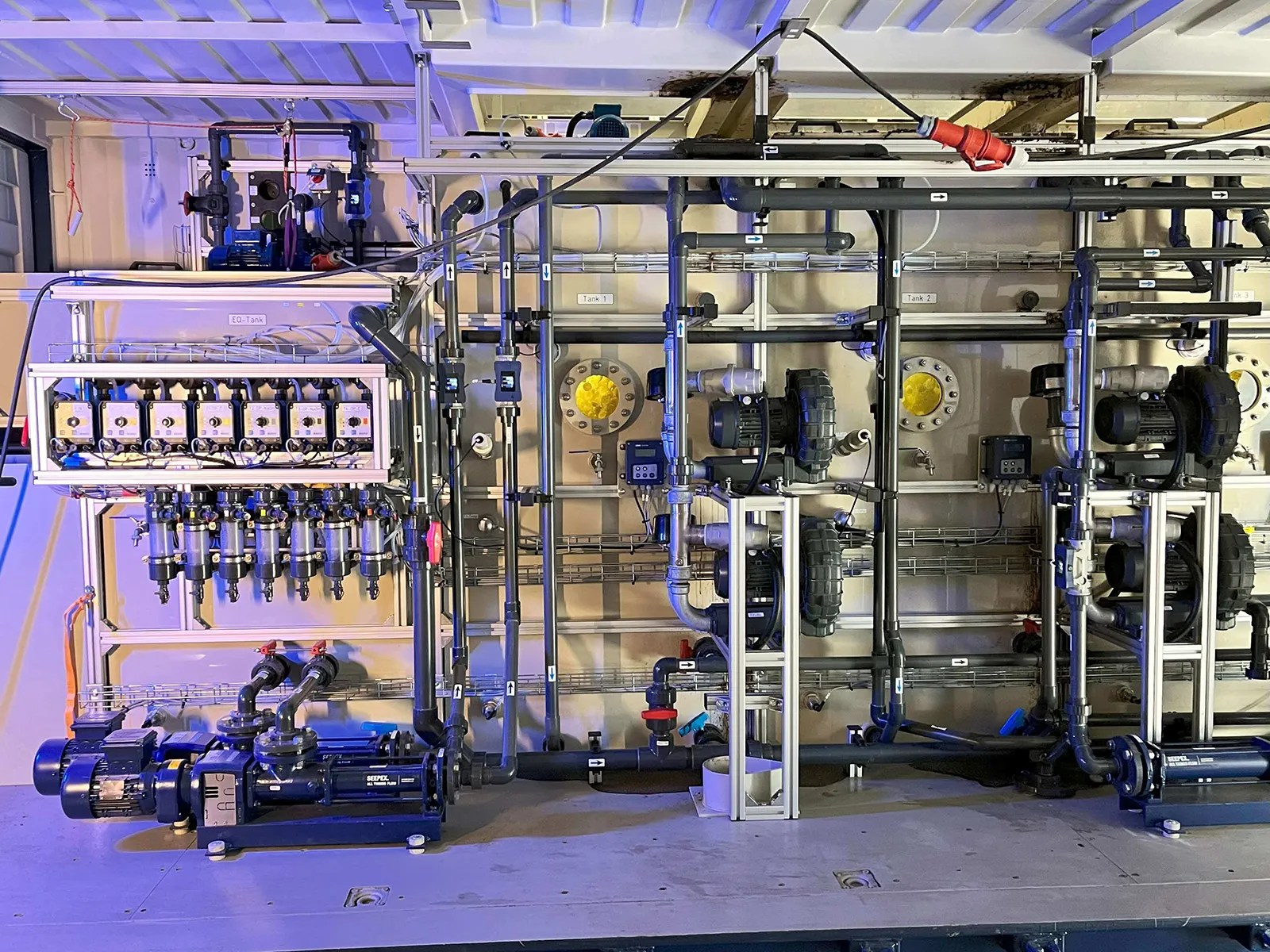
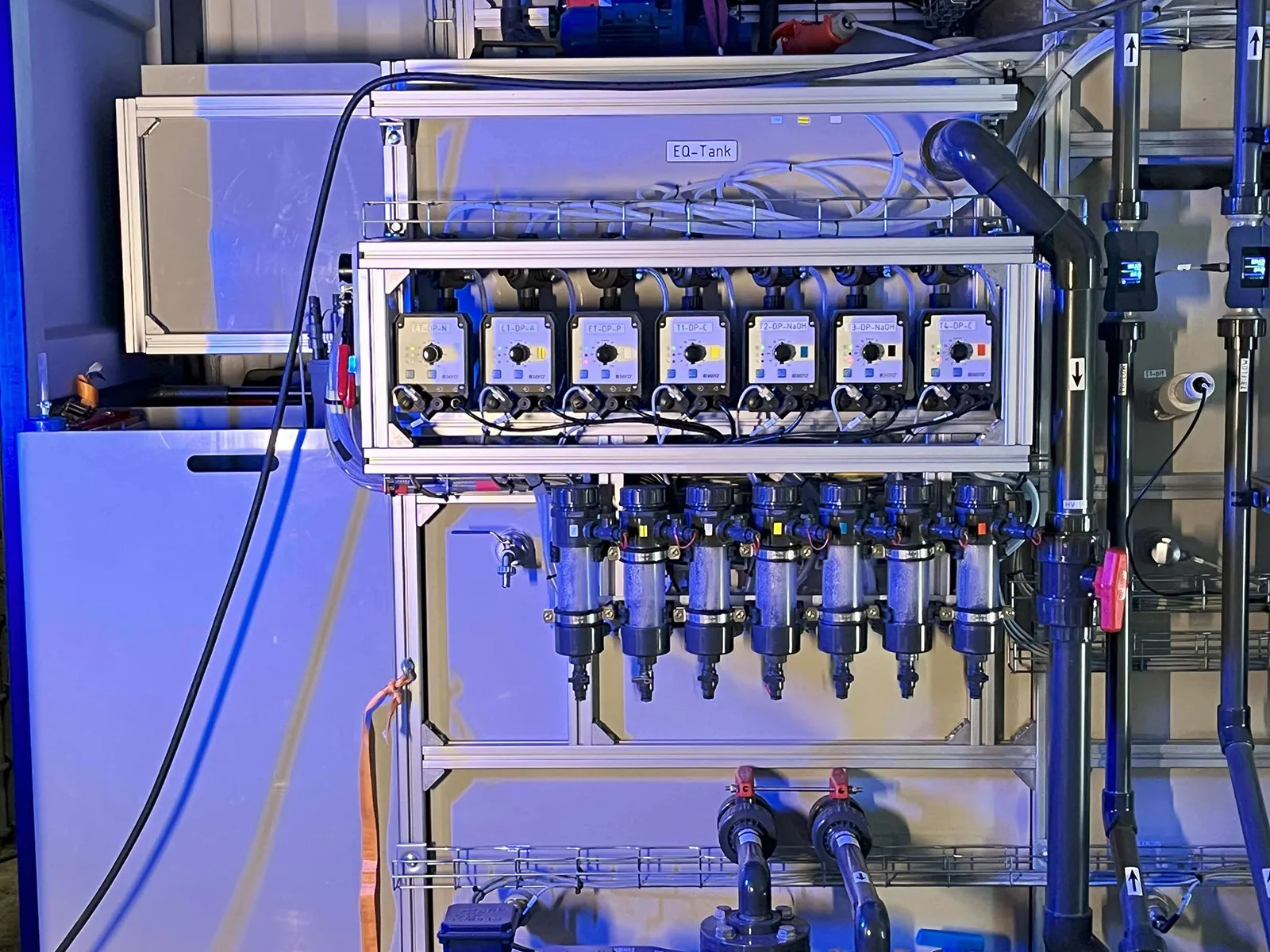
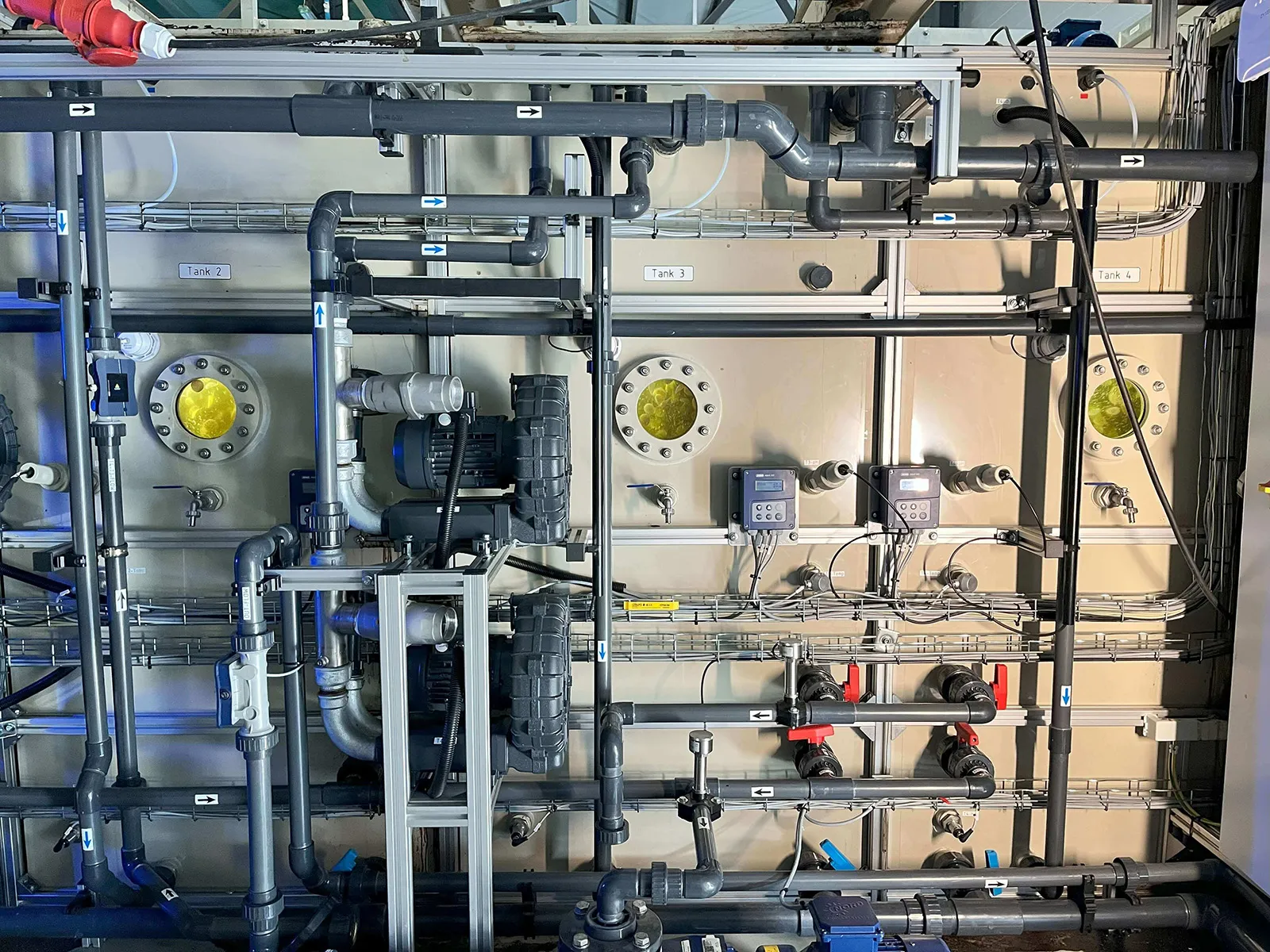
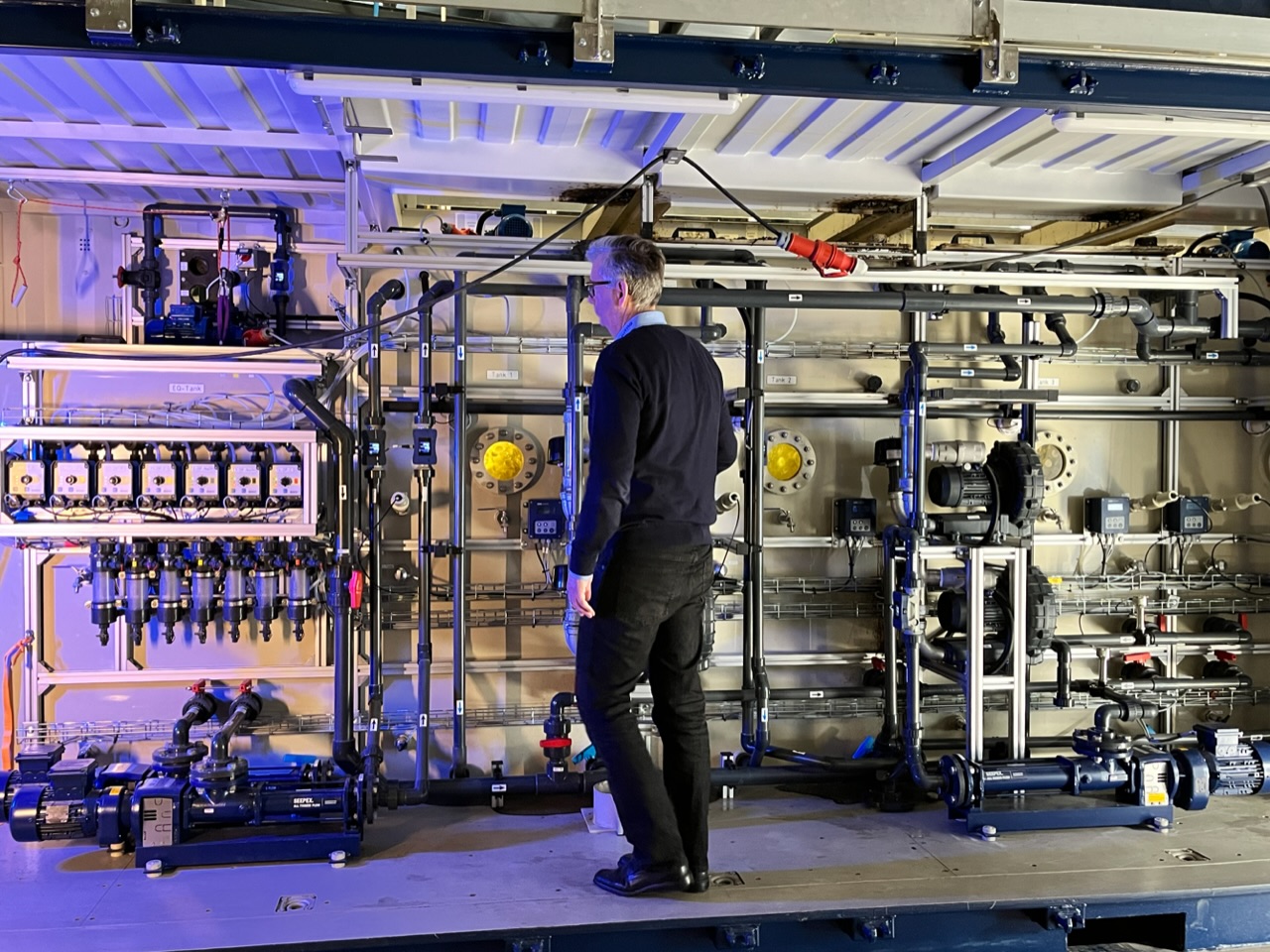
Mobile Wastewater Pilot Plant
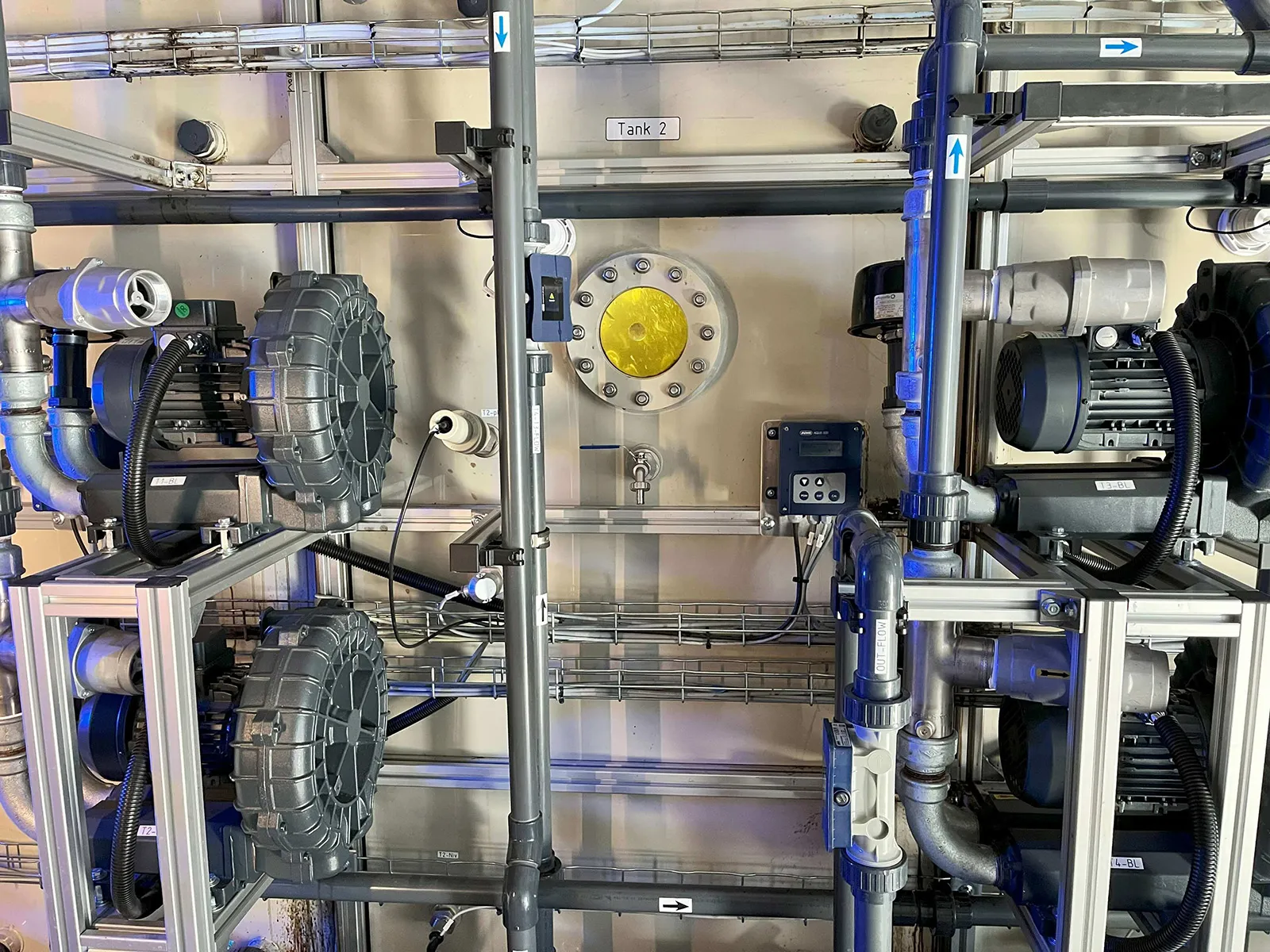
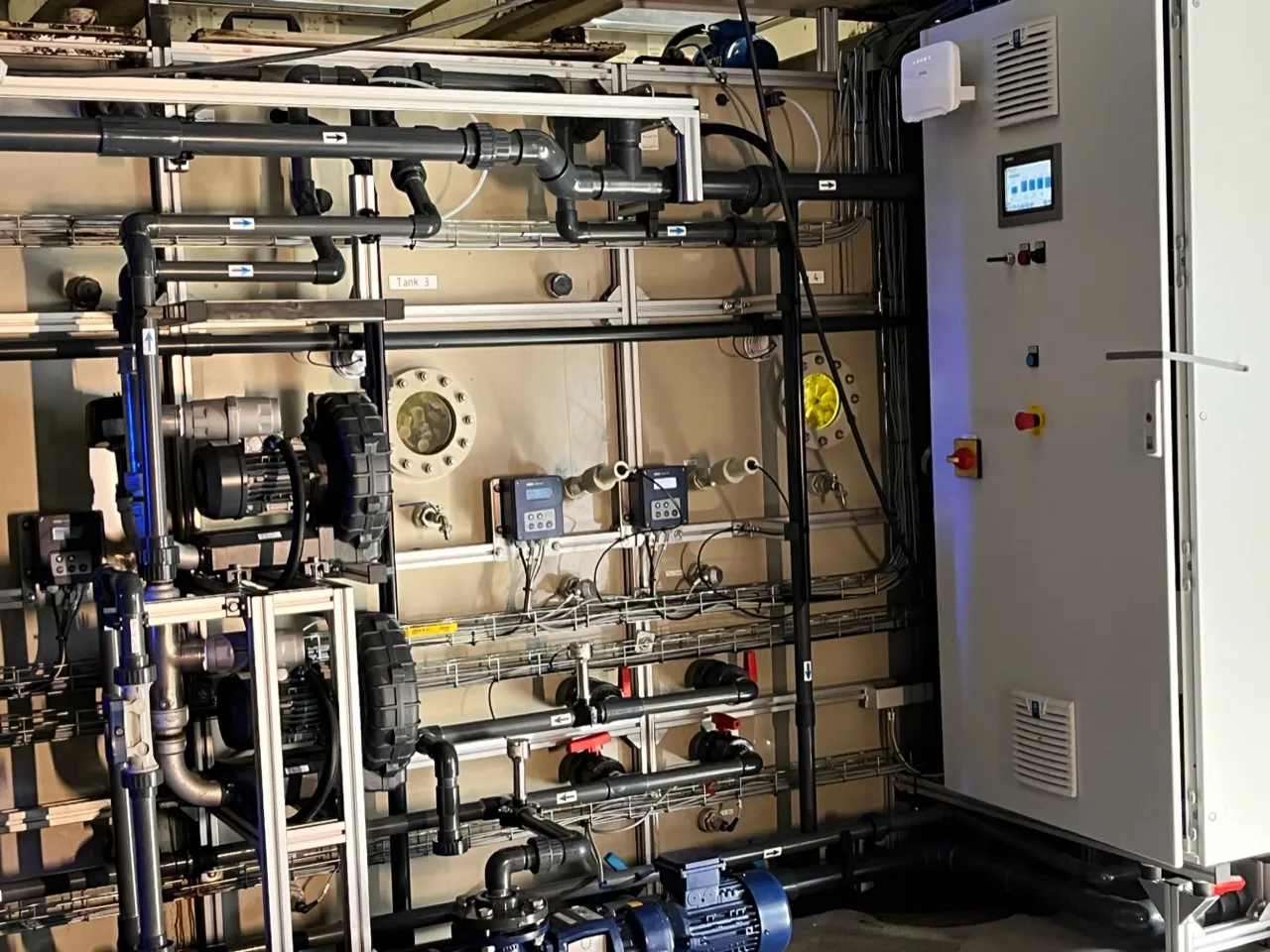
The MUTAG Pilot Plant is a cutting-edge mobile biological wastewater treatment pilot plant designed for seamless testing. Easily installable, this solution empowers our customers to evaluate our products using the specific wastewater types relevant to their needs.
It provides a unique opportunity for comprehensive comparisons, allowing informed decisions and strategic investments.
Primarily, MUTAG Pilot Plant serves as a testing ground for new process concepts, establishing a dependable data foundation for future process scaling. Simultaneously, it assesses the feasibility of biological wastewater treatment across various applications.
Investment evaluation
Evaluating a substantial investment before final commitment.
Exploring alternatives
Exploring alternatives when the existing biological treatment system is no longer effective.




.jpg)